Analysis of the Transformer architecture
Research Transformer AI
Natural Language Processing and the Transformer Architecture
The Transformer architecture was first introduced in the 2017 paper “Attention Is All You Need”. Previously, RNN and LSTM, which were mainly used in the field of natural language processing, had the following problems:
- They had to process tokens sequentially, which slowed down the learning speed.
- When processing long sentences, there was a problem of forgetting tokens that were far apart from each other.
The Transformer architecture effectively solved these two problems, and as a result, it is still mainly used in the field of natural language processing today. Most LLMs, such as GPT family starting with GPT-2 and LLaMA, also used the Transformer architecture. (In the case of models that generate responses, they often seem to have a decoder-only structure.)
Transformer Architecture Explanation
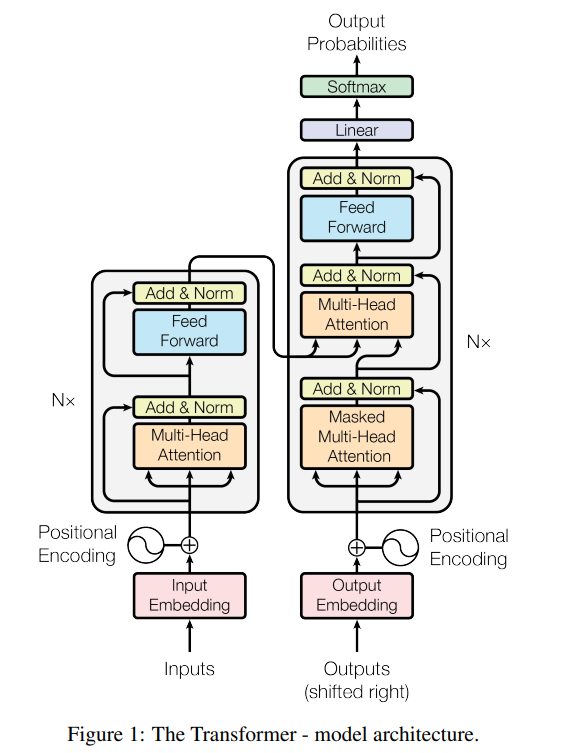
model architecture
The left is the encoder, the right is the decoder.
Input Embedding
Converts tokens, which are strings recognizable by humans, into multi-dimensional vector values that can be recognized by a machine.
e.g.,
I -> [1, 0],
love -> [2, 3],
only -> [4, -2],
you -> [-1, -3]
Positional Encoding
I love only you, Only I love you
They are made up of the same words, but the order of the words makes them completely different sentences.
Even with the same word, its position in the sentence affects how the sentence is interpreted.
In other words, word order is important in language.
Therefore, Positional Encoding is additional information to indicate where a token is located in a sentence.
\[PE(pos, 2i) = sin\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{2i}{d_{\text{model}}}}}\right)\] \[PE(pos, 2i+1) = cos\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{2i}{d_{\text{model}}}}}\right)\]In the paper “Attention Is All You Need”, the position information is incorporated by adding values from trigonometric function with varing frequencies-determined by the token’s position (pos) and the vector dimension (i)-to the previous input embedding result.
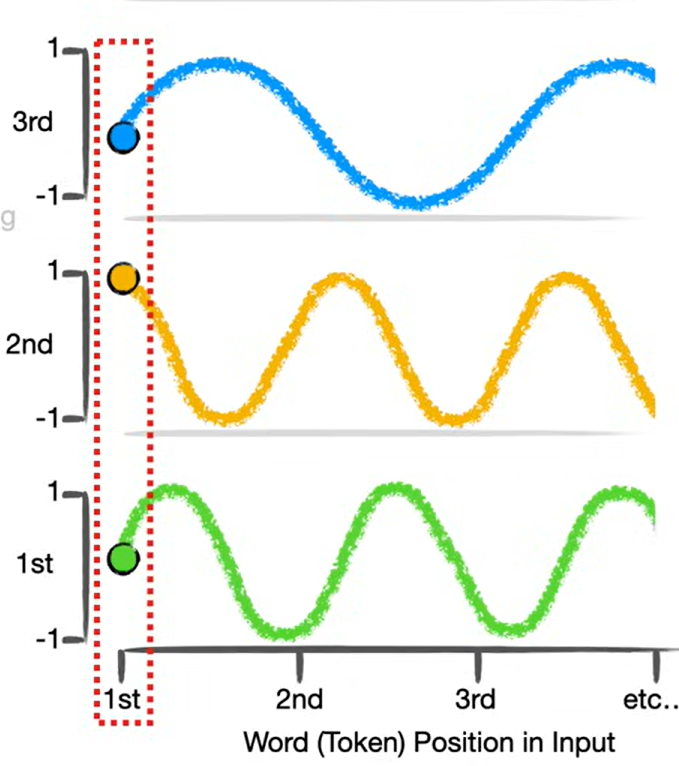
e.g.,
Assume the Positional Encoding value for the first token is [0, 1]
The Positional Encoding value for the second token is [-0.93, 0.1]
The Positional Encoding value for the third token is [-0.87, -0.9]
The Positional Encoding value for the fourth token is [0.2, 0.8]
The third token in “I love only you” which is “only” becomes [4, -2] + [-0.87, -0.9] = [3.13, -2.9] when the PE value is added.
The first token in “Only I love you”, which is “only”, becomes [4, -2] + [0, 1] = [4, -1] when the PE value is added.
Thus, the same word can have different values based on its position. In other words, it reflects the position information in the sentence.
Self-Attention (Multi-Head Attention)
Words are influenced by the other words that make up a given sentence.
The pizza came out of the oven and it tasted good.
In the given sentence, “it” is a pronoun that refers to a noun, so it could be “pizza” or “oven”.
However, we know that “it” is “pizza”. The reason is that we have seen the context of the entire sentence.
In other words, this means that the token “it” can understand the context of the sentence by calculating its relationship with all the tokens that make up the sentence, including itself. The mechanism by which each token calculates its importance with all the tokens that make up the sentence to understand which tokens are important and the context of the sentence is called Self-Attention.
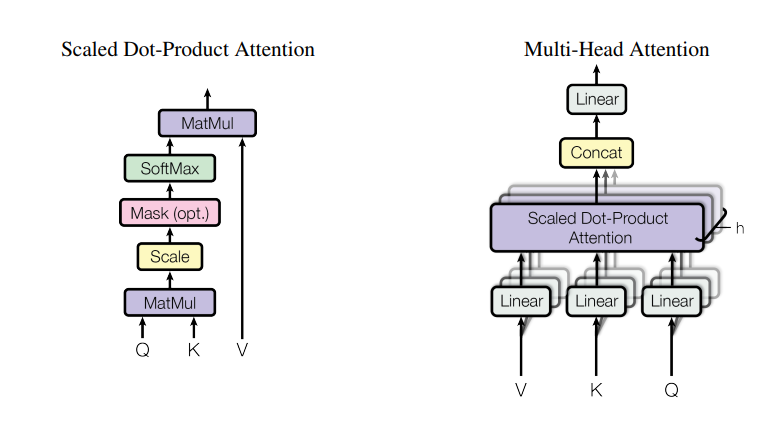
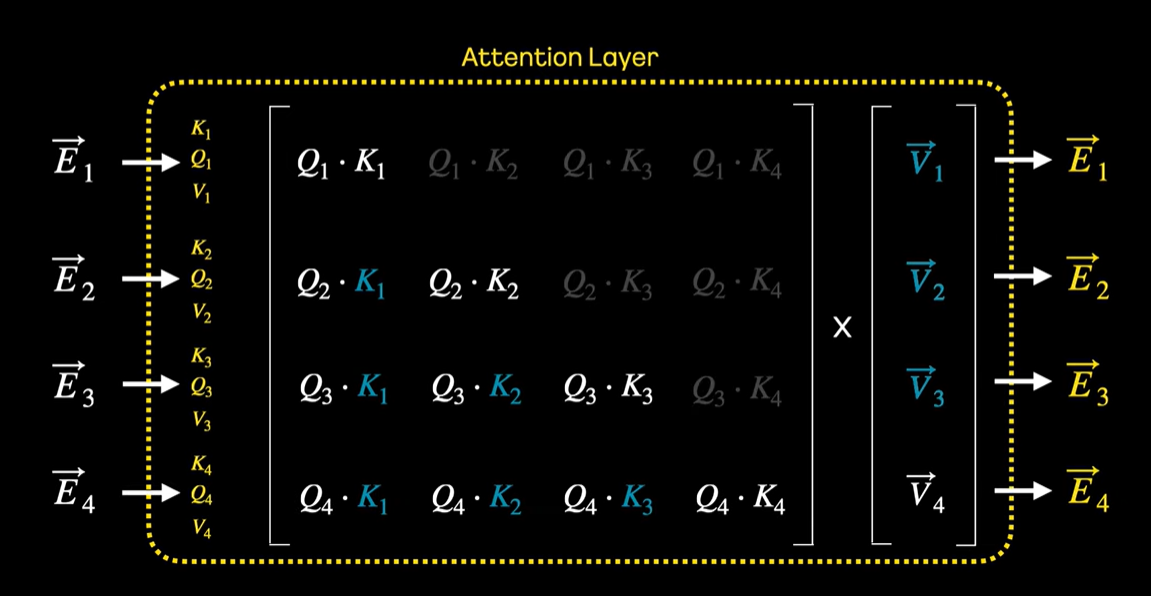
Scaled Dot-Product Attention
Each component of the Multi-Head Attention layer, and the smallest basic unit for calculating Self-Attention, is the Scaled Dot-Product Attention. Three important terms appear here.
- query
- A vector produced by applying a weight to the sum of the token embedding result and its positional encoding.
- key
- In the same way as the query, another weight is multiplied to obtain the key.
- value
- In the same way as the query and key vectors, another weight is multiplied to obtain the value.
- A vector that represents the characteristics of a word.
After scaling the vectors obtained by taking the dot product of the query with the key of other tokens so that they do not become too large, they are passed through the SoftMax function to be normalized as probabilities. By multiplying this normalized probability by the value of each token, the importance between the tokens is finally calculated.
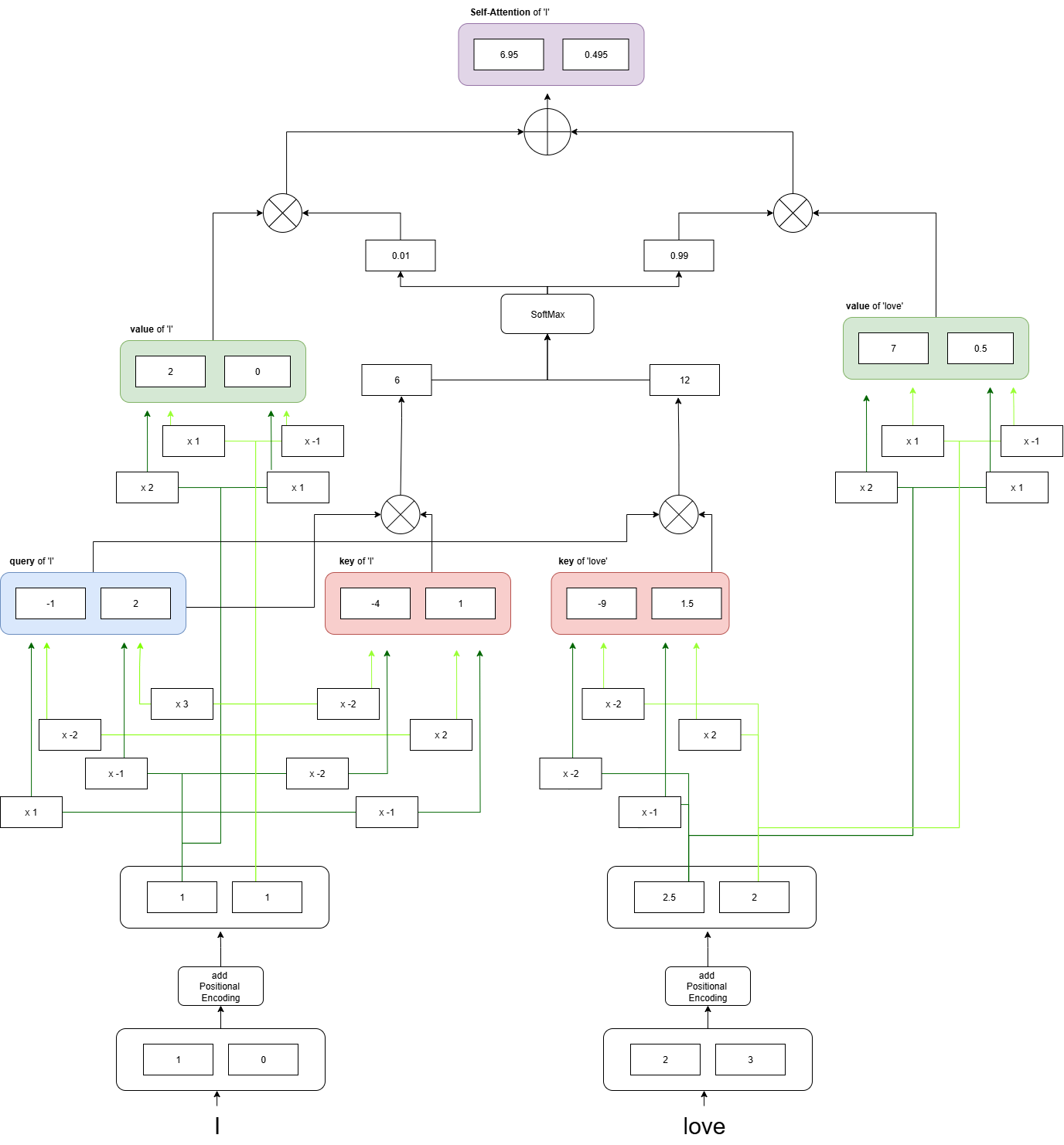
Scaling omitted
The weights for calculating the query are the same regardless of the token.
The weights for calculating the key are the same regardless of the token.
The weights for calculating the value are the same regardless of the token.
Since the key and value are fixed vectors for each token, there is no need to recalculate the key and value for each query. Therefore, by storing the key and value in memory after their initial computation for the first query, subsequent attention operations can be performed more efficiently. Storing the key and value in this way is called KV Cache.
Mask
The decoder must have an auto-regressive property, feeding its previous outputs back as inputs to generate responses. Therefore, tokens earlier in the sequence should not be influenced by tokens that come later. In other words, the attention values of preceding tokens must not be altered by subsequent tokens.
To achieve this, the dot product with the keys of future tokens is deliberately masked with negative infinity, preventing later tokens from having any effect. In summary, to generate the n-th token, the decoder only considers tokens from position 0 to n.
Conclusion
The Transformer has made advancements in two major aspects compared to RNN and LSTM.
-
Through positional encoding, it became possible to add the order information within a given sentence all at once. The self-attention mechanism can calculate the relationships between each token at once, regardless of the distance between tokens in the sentence. Therefore, it solved the problem of inefficient information transfer when tokens are far apart within a sentence.
-
Through the self-attention mechanism, it became possible for all tokens within a sentence to calculate their relationships simultaneously and in parallel, regardless of the sentence order. This enabled parallel computation on GPUs, leading to faster training speeds compared to previous models like RNN that processed sequentially.